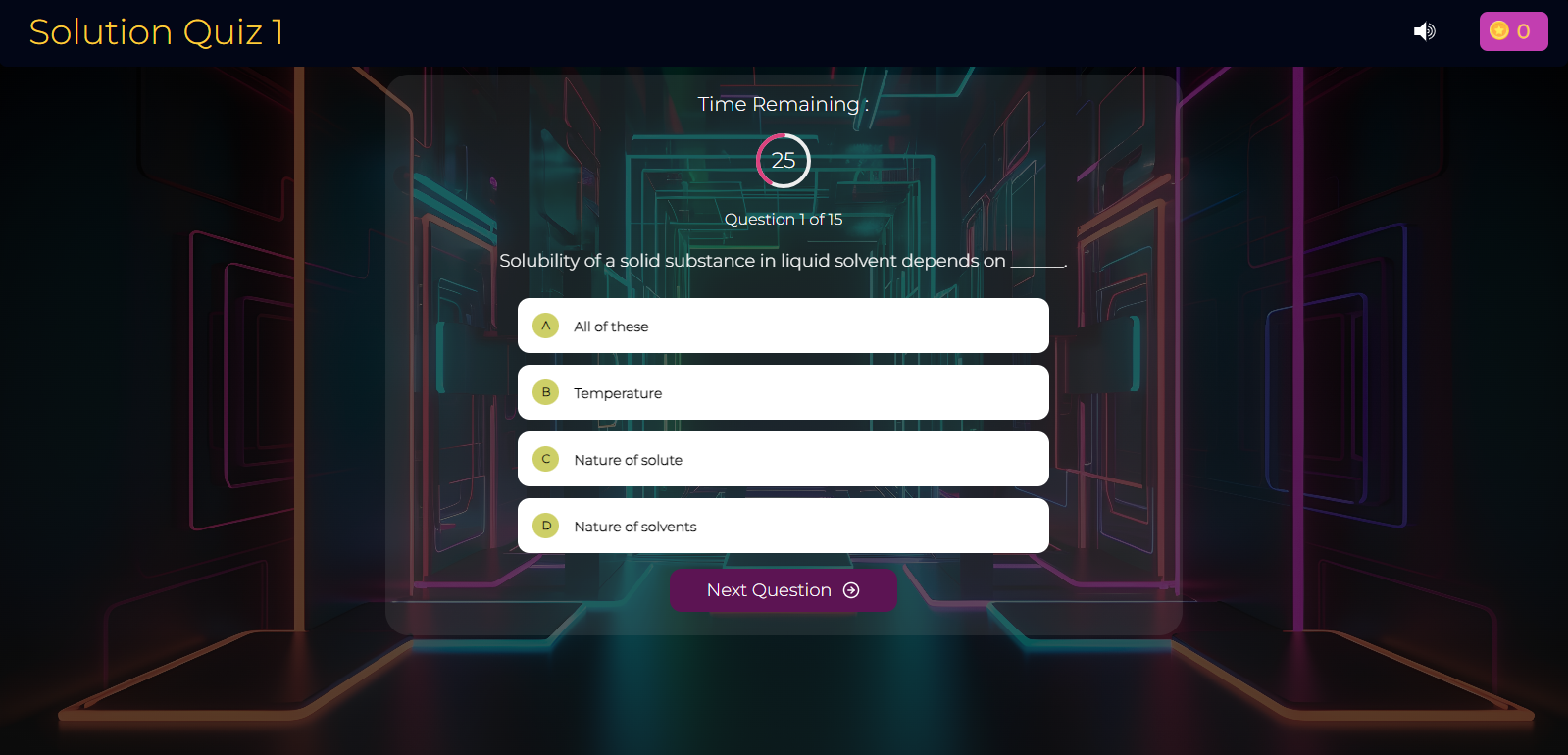
Optics Quiz-1
Popular Questions In Optics Quiz-1
A ray of light propagating along the direction is incident on a plane mirror. After reflection, it moves along the direction . The angle of incident is
A spherical lens forms an image, twice the length of the object, on a screen. The distance between the object and the screen is 120 cm. The power of the lens, is (nearly)
The focal length, of a thin biconvex lens, is 20 cm. When an object is moved from a distance of 25 cm in front of it to 50 cm, the magnification of its image changes is to . The ratio is
A convex lens is in contact with a concave lens. The magnitude, of the ratio of their focal lengths, is . Their equivalent focal length is 30 cm. The individual focal lengths (in cm), of the two lenses, are, respectively,
An observer looks at a distant tree of height 10 cm, with a telescope of magnifying power 20. To the observer, the tree would appears.
In a Young’s double slit experiment, using monochromatic light of wavelength , the path difference (in terms of integer n), corresponding to a point, having half the peak intensity, is
A beam consists of an unpolarised and a plane-polarised part. The beam is viewed through a polarised. On rotating the polaroid through one full circle, about the direction of propagation of the beam as axis, the intensity of the transmitted light.
The headlights of a car are 1.2 m apart. They emit light of nm. The diameter of the pupil of the observer's eye is 3 mm. The maximum distance of car from observer so that the two headlights are just resolved is
A beam of unpolarised light, of intensity , is passed through a polaroid A. It is next passed through another polaroid, B, which is oriented so that its principal plane makes an angle of , relative to that of A. The intensity of emergent light is
A ray of green light is incident from water to air; (at the air-water interface) at the critical angle of incidence. Select the correct statement: